Virtualization is the creation of a digital file on your computer that looks and performs as if it is a different piece of hardware. In simpler terms, it is a virtual copy of a physical computer.
Why would you need this?
For example, let’s say that you own a Windows PC, but want to work on Mac OS. You can create a virtual version of Mac on your Windows PC without having to buy a MacBook.
This life hack can save small businesses from spending big on hardware and add flexibility to their operations. This enables one of the main benefits of virtualization is cost savings.
How does virtualization work?
Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based, or "virtual" version of a computer, with dedicated amounts of CPU, memory, and storage that are "borrowed" from a physical host computer.
It makes it possible that any OS can run on top of any other physical host machine.
The VM is partitioned from the rest of the system, meaning it's completely isolated and can't interfere with the host computer's primary OS.
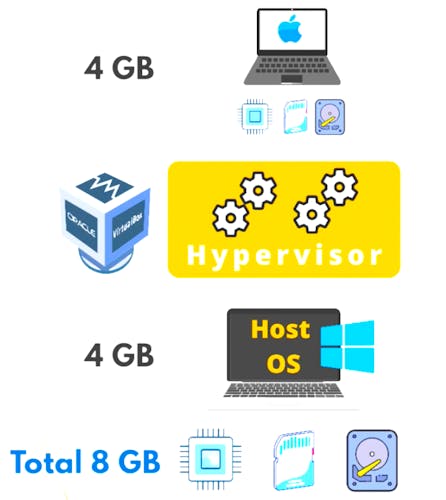
The hardware resources are shared among Guest and Host OS. So you can only give resources you actually have.
What is a Hypervisor?
- The essential component in the virtualization stack is a piece of software called a hypervisor.
- As virtualization allows for a fast switch between different operating systems.
- To make this switch possible, a system needs a hypervisor. This is a thin layer of software that allows one physical computer to run different operating systems alongside each other.
- Hypervisor works as a traffic guard that assigns each operational system its place in the storage and portion of power.
- One of the most popular hypervisor is open-source Oracle VM VirtualBox.
Virtual Machine is commonly shortened to just "VM"
Host OS vs Guest OS
- Host OS = runs directly on the hardware
- Guest OS = runs on the virtual machine
Types of Hypervisor
There are two distinct types of hypervisors used for virtualization - type 1 and type 2:
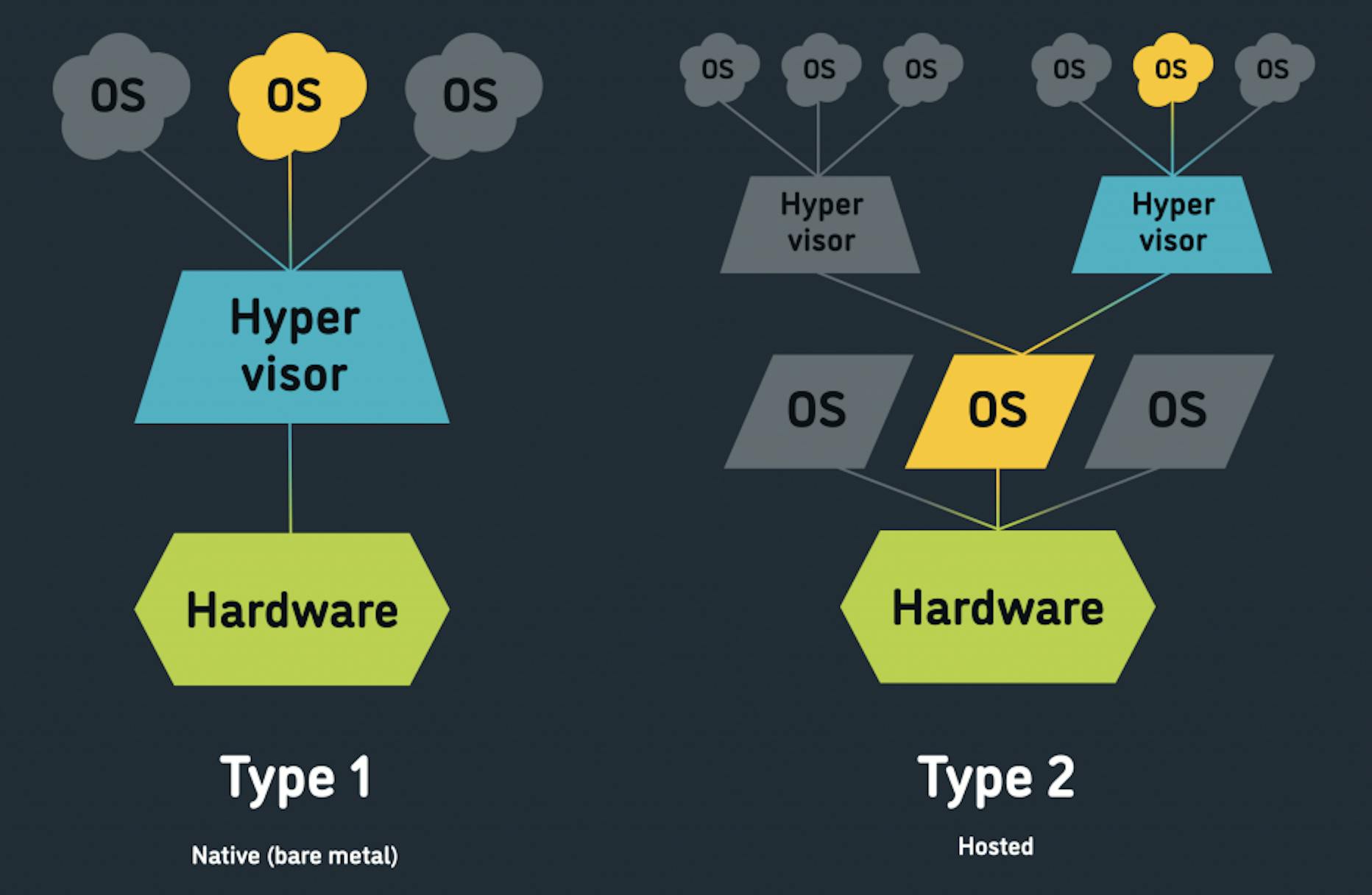
Type 1 (Native)
- That run directly on the host's hardware to control the hardware, and to monitor the guest OS.
- The guest OS runs on a separate level above the hypervisor.
- USE CASE: Efficient usage of hardware resources (e.g. cloud provider)
- Examples of this classic implementation of VM architecture are Oracle VM, Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware ESXi.
Type 2 (Hosted)
- Designed to run within a traditional OS.
- A hosted hypervisor adds a distinct software layer on top of the host OS, and the guest OS becomes a third software level above the hardware.
- USE CASE: Learn and experiment, test your app on different OS and backing up your existing OS.
- Examples: Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMware Server, Microsoft Virtual PC, KVM, QEMU, and Parallels.
Why companies adopt Virtualization?
Main benefit: Instead of OS being tightly coupled to the hardware.Virtualization gives an abstraction layer, with the following benefits:
Security: Secure very easily.
Agility and speed: Spinning up a VM is easy and quick, compared to setting up an entire new server.
Cost savings: Efficient usage of hardware resources
Portable: OS as a portable file (VMI - Virtual Machine Image).
